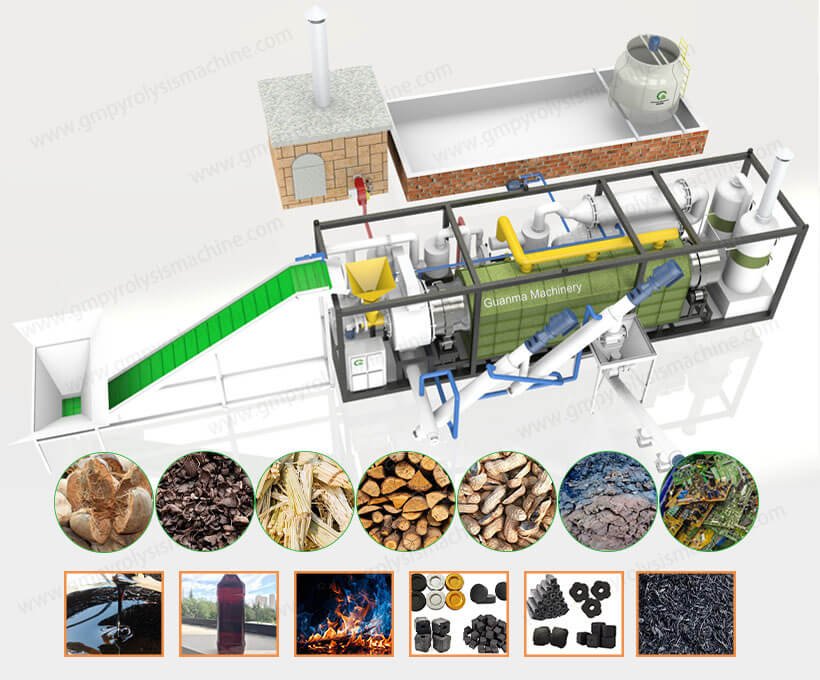
Carbonation Machine for Biomass Processing
A carbonation machine (also called a biomass carbonization reactor) is an industrial system that transforms organic waste into stable biochar through oxygen-limited thermal decomposition. Unlike beverage carbonators, these machines use pyrolysis technology to convert agricultural residues, wood waste, or sewage sludge into carbon-rich biochar – a valuable product for soil enhancement, carbon sequestration, and industrial applications.
Understanding how these specialized systems work is essential for maximizing biochar yield, optimizing energy efficiency, and meeting emission standards in sustainable waste management.
Core Components of a Biomass Carbonation Machine
Industrial biomass carbonators integrate these critical subsystems:
Preprocessing Unit
Crusher & Dryer: Reduces feedstock size (<20mm) and moisture (<15%)
Feeding System: Automated conveyors for continuous carbonization
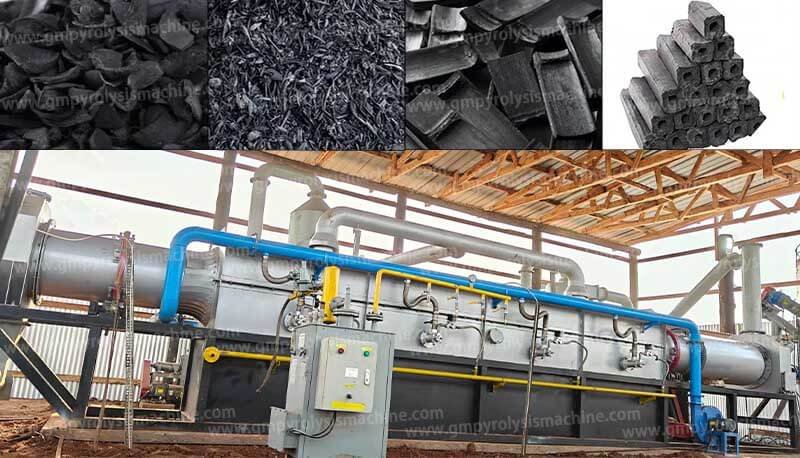
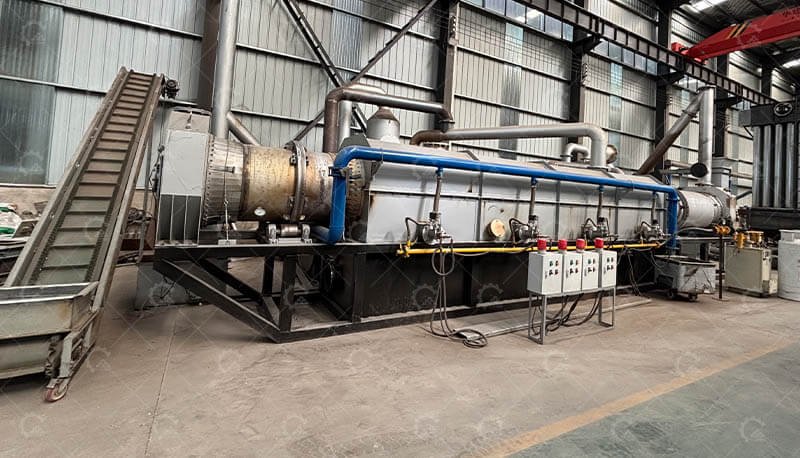
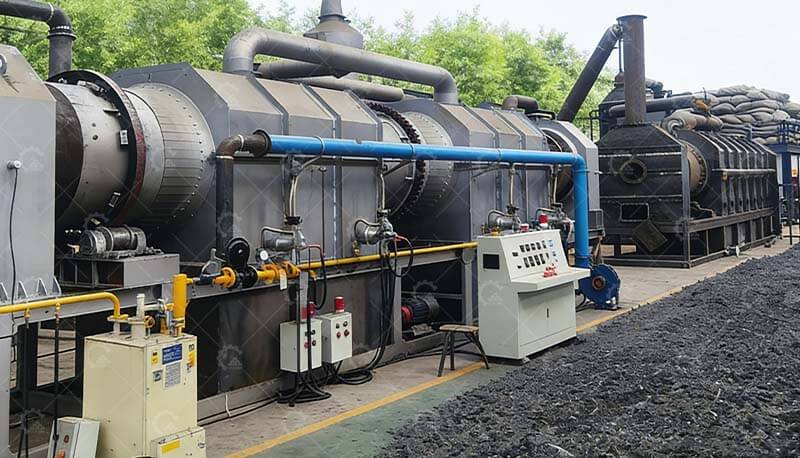
Pyrolysis Reactor
Rotary Kiln (for uniform heating) or Retort Chamber (for high-purity biochar)
Temperature Zones: Preheating (150-300°C), Carbonization (400-700°C), Cooling
Gas Recycling System
Syngas Condensers: Capture wood vinegar & tar
Thermal Oxidizer: Burns combustible gases to power the reactor
Emission Control
Cyclone Dust Collector: Removes particulate matter
Wet Scrubber: Neutralizes acidic gases (HCl, SO₂)
Biochar Processing
Quenching Tank: Rapidly cools biochar
Pelletizer: Compacts finished product
The Biomass Carbonation Process: Step-by-Step
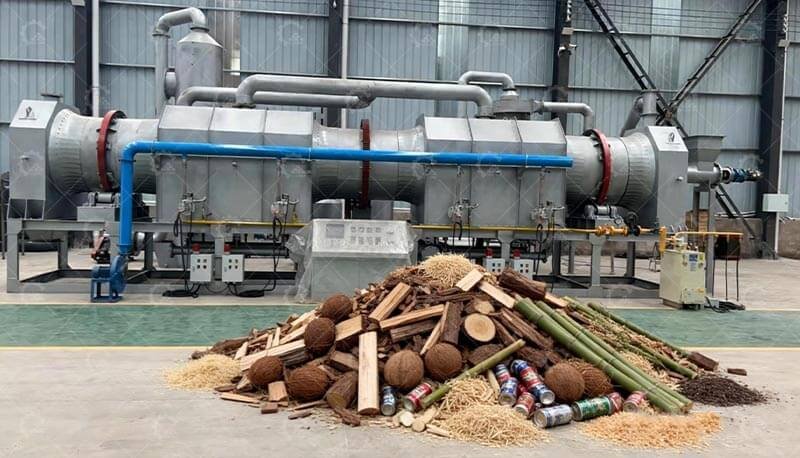
1. Feedstock Preparation
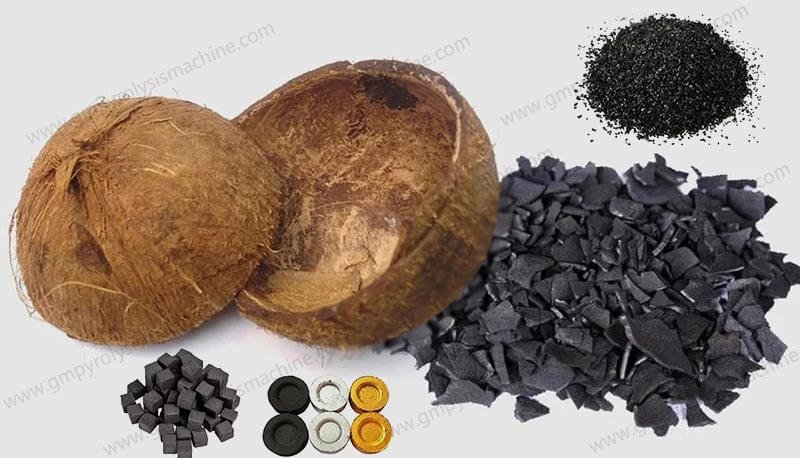
Biomass shredding: Reduces coconut shells/wood chips to 10-15mm particles
Drying: Lowers moisture to <15% using flue gas heat recovery
Critical for efficiency: 1% moisture reduction = 5% energy savings
2. Oxygen-Free Pyrolysis
Biomass enters the reactor at 15-30 RPM rotation speed
Three-stage temperature control:
Dehydration (200°C): Removes residual moisture
Volatiles Release (300-500°C): Breaks down hemicellulose/cellulose
Carbonization (500-700°C): Forms stable carbon structures
3. Gas Treatment & Energy Recovery
Syngas passes through:
Condensation Tower: Separates wood vinegar (pH 2-3) and bio-oil
Gas Holder: Stores combustible gases (CH₄, H₂, CO)
Burner: Recycles 60-70% energy to sustain pyrolysis
4. Biochar Stabilization
Rapid Cooling: Prevents spontaneous combustion
Activation (optional): Steam treatment increases surface area to 400-800 m²/g
Choosing Guanma Machinery Carbonation Machine: 5 Critical Factors
Feedstock Type
Woody biomass: Requires rotary kilns
Wet sludge: Needs pre-drying & retort reactors
Capacity Requirements
Mobile Biochar MakingMachine: 500 kg/day (modular units)
Continuous Carbonization Pyrolysis Machine: 20+ tons/day (continuous systems)
Operational Data: Efficiency Benchmarks
Energy balance: 1 ton biomass → 300kg biochar + 200kg wood vinegar + 1,500kW energy
Carbon sequestration: 2.5-3.0 tons CO₂e per ton biochar
ROI period: 18-24 months for 5 T/day systems
Transforming Waste into Value
Biomass carbonation machines turn low-value organic residues into high-demand biochar while reducing carbon footprints. By mastering the interplay between temperature control, residence time, and gas recycling, operators achieve both environmental compliance and economic profitability.
Ready to optimize your biomass conversion? Contact us for solutions!